What Are OOP Concepts?
With programming, we have to consider the basic concepts of OOP (Object oriented Programming). OOP allows us to understand our code more in depth and better understanding within the algorithm from a mathematical perspective.
How can we implement OOP conceptionally and effectively to our algorithm?
We can implement Object Oriented concepts by understanding the basics of Software Architecture. The primary goal of software architecture is to define the non-functional requirements of a system and define the environment. The detailed design is followed by a definition of how to deliver the functional behavior within the architectural rules.
What is Software Architecture?
Software Architecture refers to the high level structure of a software system and the discipline of creating such structure and system. In layman’s terms, software architecture is the process of software converted to structured solution that meets the technical standard of what the businesses need. This means that we are asked about the characteristics of a software that can affect any form of software architecture design. For further explanation, software characteristics are described as what kind of requirements or expectations that the software is in a technical or operational level. Whenever a owner or manager of a company says that he or she is competing in a highly, rapidly evolving market, he or she wants the outcome of the model to be adaptable as quickly as possible. With any software works, it should be “extendable, modular, and maintainable” if a company deals with urgent requests that need to be solved successfully in a matter of time. Performance and reliability are the key characteristics of any software developer.
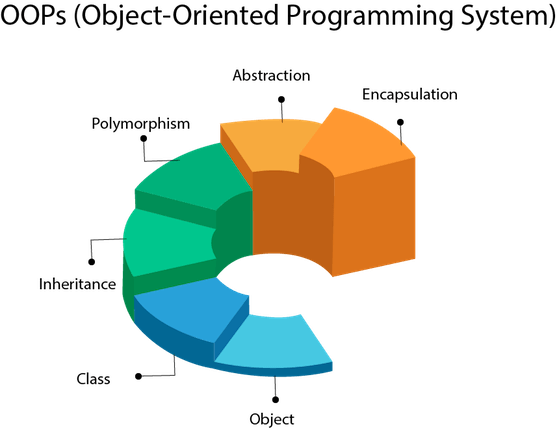
The four “GOLDEN” words of OOP concepts.
In a object oriented programming language such as Java, it is important to understand to model that OOP is provided for us. These model consists of Abstraction, Encapsulation, inheritance and polymorphism. OOPS is all about developing a program that can access to their unique properties and the plausible operations in their own way.
Abstraction
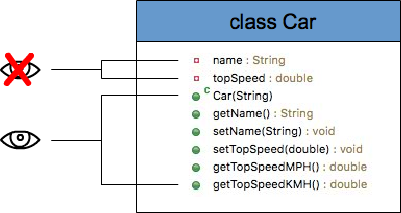
The first fundamental concept of OOPs is Abstraction. Abstraction is the process in which you show only the relevant data and hide the unnecessary details of an object from the user.
Encapsulation
Encapsulation is one of the fundamentals of OOP (object-oriented programming). It refers to the bundling of data with the methods that operate on that data.
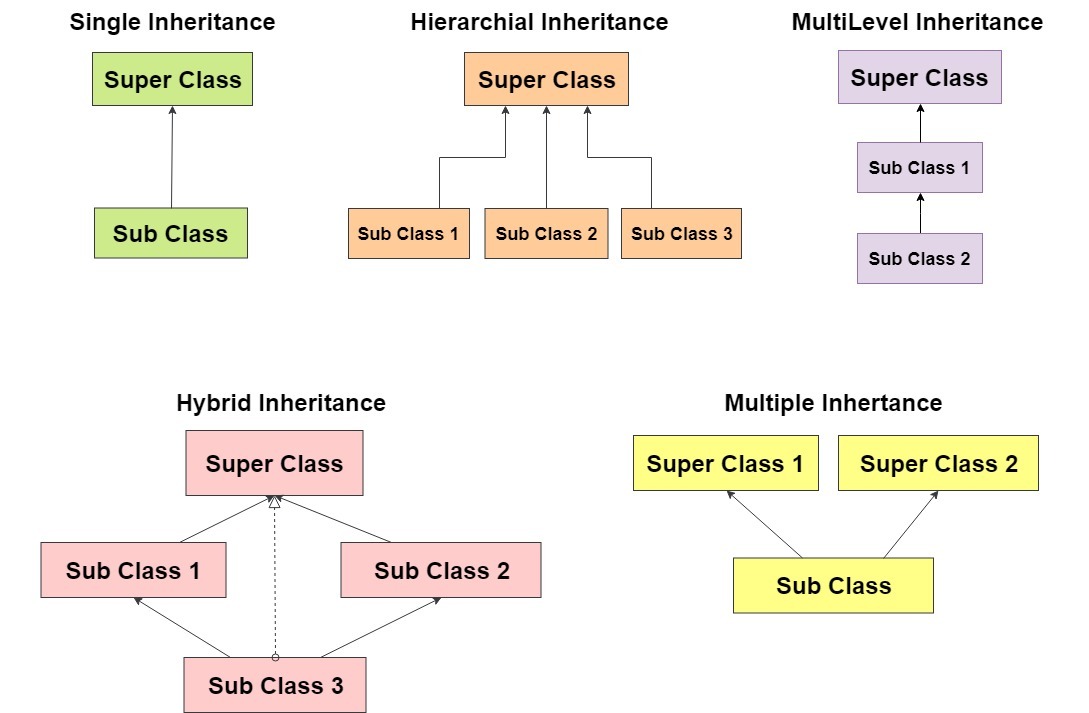
Inheritance
Inheritance is one of the core concepts of Object-Oriented Programming regarding to deriving from class for a hierarchy of classes that share the same attributes, methods, and similar sets of algorithm.
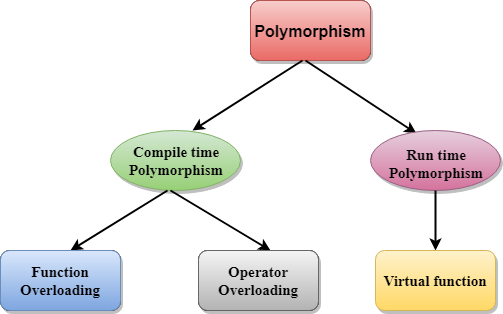
Polymorphism
Polymorphism is the provision of a single interface to entities of many different types from the data. This applies to object oriented programming a lot when many subclasses of the class are define from their own unique behaviors.